Northern Hayward Fault Network Overview


The BSL operates a number of stations in the Bay Area with seismic and other geophysical sensors in boreholes. They are tools for observing tiny earthquakes and other deformation signals that may hint of incipient seismic movements. If the instruments were installed near the surface, cultural noise (vibrations from vehicles and other human sources) would overshadow the tiny signals that we wish to study. The funding for these stations comes from a variety of sources. A number of the stations were installed as part of a joint project with the USGS to monitor the Hayward Fault, and are installed along its northern end (Northern Hayward Fault Network). A second set of stations, which include geodetic observations, were installed around the Bay to support the study of the three-dimensional strain field resulting from deformation acrosss the boundary between the Pacific and North American plates. These stations have been called "mini-PBO" stations. Finally, a number of stations are located and supported by the California Department of Transportation. Seismic data from the downhole geophones and accelerometers at all these stations are integrated into the holdings for the Berkeley Digital Seismic Network and contribute to real-time monitoring of earthquakes in the Bay Area, and to other research and monitoring activities.
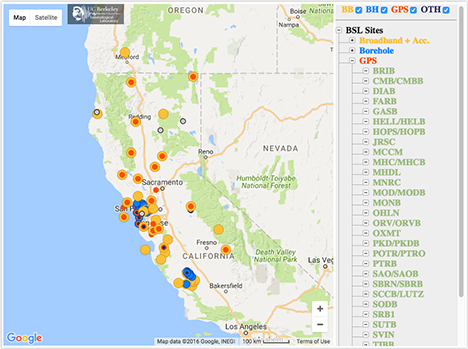
- Map of borehole stations
- Table of borehole stations
- BK Information Directory, including
- List of station locations
- List of available channels
- Instrument Response
- Querying the archives
- Access data through NCEDC web services
- Requesting data by channel and time
- Requesting data by event
- U.S. Geological Survey
- Caltrans
- Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI)
- University of California Campus/Laboratory Collaboration (CLC)
- Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (LBNL)
- Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL)
3-component tensor strainmeter (designed and built by CIW)
3-component geophones (Oyo 4.5 Hz or Mark Products)
3-component Wilcoxon accelerometers
Atmospheric pressure
Pore Pressure
Geodetic GPS
Heat flow
Tiltmeter
24-bit Quanterra digital data logger and a 18-bit ZENO-3200 data logger
GPS clock
Continuous telemetry to UC Berkeley
Backup power supply
| Sensor | SEED Channels | Rate (samples/sec) | Sampling Mode | FIR Filter |
| Geophone | EP1, EP2, EP3 | 100.0 | Triggered | Causal |
| Geophone | DP1, DP2, DP3? | 500.0 | Triggered | Causal |
| Accelerometer | LL1, LL2, LL3 | 1.0 | Continuous | Acausal |
| Accelerometer | BL1, BL2, BL3 | 20.0 | Continuous | Acausal |
| Accelerometer | HL1, HL2, HL3 | 100.0 | Continuous | Causal |
| Accelerometer | CL1, CL2, CL3 | 500.0 | Triggered | Causal |
Normally, only 3 channels of acceleration and the vertical component geophone are recorded and archived. In some cases, sensor failure has led to different recording combinations.
As part of this collaboration, the borehole sites will have two sets of digital data loggers. The table below lists which channels will be recorded and the SEED network and location codes which will be used.
| Sensor | Network Code |
Channel Code |
Location Code |
Rate (samples/sec) | Sampling Mode | Datalogger |
| Tensor strainmeter | UL | RS1, RS2, RS3 | T0 | 1/600 | Continuous | ZENO-3200 |
| Tensor strainmeter | BK | US1, US2, US3 | 0.01 | Continuous | Q4120 | |
| Tensor strainmeter | BK | VS1, VS2, VS3 | 0.1 | Continuous | Q4120 | |
| Tensor strainmeter | BK | LS1, LS2, LS3 | 1.0 | Continuous | Q4120 | |
| Tensor strainmeter | BK | BS1, BS2, BS3 | 20.0 | Continuous | Q4120 | |
| Tensor strainmeter | BK | HS1, HS2, HS3 | 100.0 | Continuous | Q4120 | |
| Geophone | BK | BP1, BP2, BP3 | 20.0 | Continuous | Q4120 | |
| Geophone | BK | EP1, EP2, EP3 | 100.0 | Triggered | Q4120 | |
| Atmospheric Pressure | UL | RD1 | T0 | 1/600 | Continuous | ZENO-3200 |
| Atmospheric Pressure | BK | LDO | 1.0 | Continuous | Q4120 | |
| Pore Pressure | BK | LDD | 1.0 | Continuous | Q4120 | |
| Heat Flow (?) | UL | ?? | T0 (?) | 1/600 | Continuous | ZENO-3200 |
| Tiltmeter (?) | UL | RAX, RAY (?) | T0 (?) | 1/600 | Continuous | ZENO-3200 |
Waveform data from the BK network are available in SEED format at the Northern California Earthquake Data Center.
Several tools provide access to SEED format data at the NCEDC, both in terms of querying the archives and allowing data requests.
Help on using these tools is available.
Detailed history of the development of the Northern Hayward Fault, Mini PBO, and annual report.
The Northern Hayward Fault Network (NHFN) is one of several networks of seismic instrumentation in northern and central California operated by the Berkeley Seismological Laboratory. Operations are partially supported by the USGS. The NHFN is an array of borehole instrumentation deployed in the San Francisco Bay Area, with the goal of monitoring microseismicity on the Hayward fault. Data from these stations are transmitted to UC Berkeley using continuous telemetry and are analyzed for earthquakes. 7 sites are currently operational and additional stations are planned.
The Integrated Instrumentation Program for Broadband Observations of Plate Boundary Deformation, commonly referred to as ``Mini-PBO'', is a joint project of the BSL, the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) at Menlo Park, the Department of Terrestrial Magnetism at Carnegie Institution of Washington (CIW), and the IGPP at UC San Diego (UCSD). It augments existing infrastructure in central California to form an integrated pilot system of instrumentation for the study of plate boundary deformation, with special emphasis on its relation to earthquakes. This project is partially funded through the EAR NSF/IF program with matching funds from the participating institutions and the Southern California Integrated Geodetic Network (SCIGN).
The project has three components. One is focused on the San Francisco Bay area, and augments existing instrumentation along the Hayward and San Andreas faults with up to 8 sites with borehole tensor strainmeters and seismometers, downhole pore pressure and tilt sensors, and geodetic GPS receivers. The second component of this project is to link the BARD network in central and northern California to the SCIGN network in southern California through the installation of 9 continuous GPS sites in the Parkfield area of central California. The third component is InSAR and supports the skeleton operations of a 5-m X-band SAR downlink facility in San Diego to collect and archive radar. In addition, some funds are used to develop an online SAR database for WInSAR users.
As part of the first component, four borehole sites were drilled during the summer/fall of 2001, at Ohlone Park (OHLN) in Hercules, on San Bruno mountain (SBRN) near Brisbane, at the Marin Headlands (MHDL) in Golden Gate National Recreation Area, and on Ox Mountain (OXMT) near Half Moon Bay. Two of these sites have been instrumented with newly fabricated borehole tensor strainmeters and seismometers, and downhole pore pressure and tilt sensors will be added in the near future.
The NHFN has been developed by the Berkeley Seismological Laboratory in collaboration with:
As described about, the Mini-PBO is a collaborative experiment among